GNN for positive selection detection
Decoding Positive Selection in Mycobacterium tuberculosis with Phylogeny-Guided Graph Attention Models
Developed a graph attention network (GAT) model that integrates phylogenetic tree structure and SNP presence to detect positively selected mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Leveraged attention-based deep learning to focus on topologically informative regions within evolutionary graphs, enhancing interpretability and biological relevance.
Achieved strong performance, and identified high-confidence adaptive mutations previously classified as uncertain by WHO.
Demonstrated the model’s capability to uncover novel resistance markers and support long-term genomic surveillance in TB.
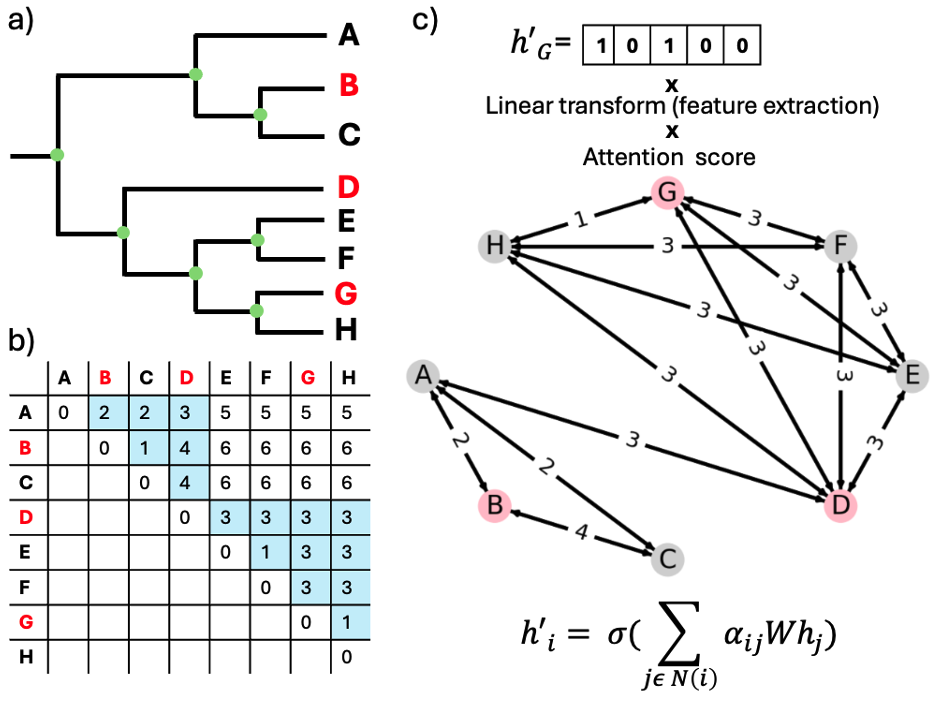
Phylogeny-informed graph construction and node feature propagation using attention-based graph neural networks
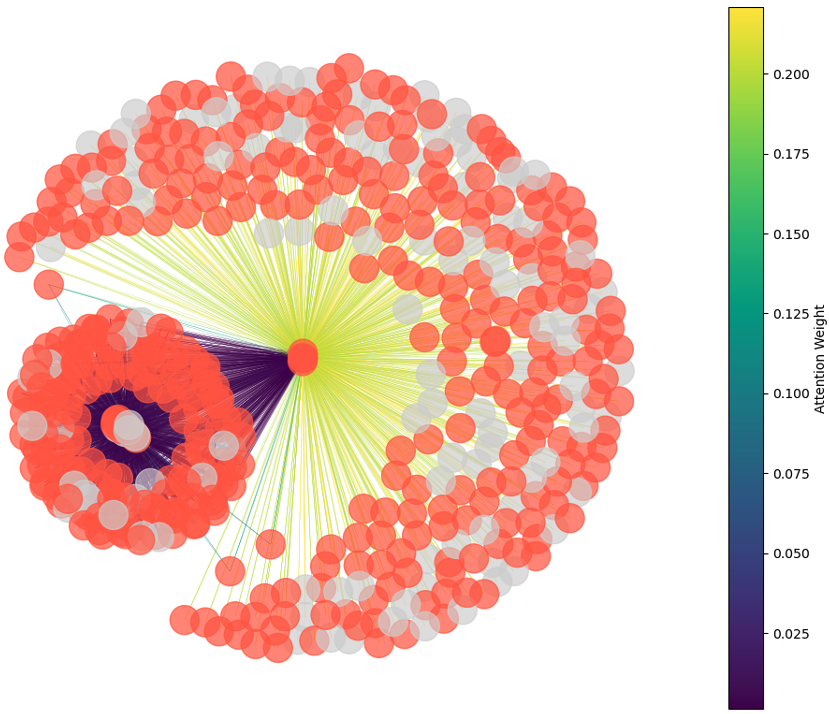
edge-level attention weights in the first GAT layer for mutation network plot corresponding to the rpob-p.Ser450Leu mutation (red: mutation present, grey: mutation absent). High attention (yellow/green)